A smart home provides great opportunities for saving resources and reducing utility costs. Let’s explore specific examples and calculations that prove the efficiency of such systems.
- Electricity Savings
- Automated Lighting: Installing motion and light sensors allows lights to turn off automatically in empty rooms and adjust brightness based on natural light. This can reduce electricity consumption for lighting by 15–20%.
- Climate Control Management: Integrating smart thermostats and motion sensors enables automatic heating and cooling regulation based on occupancy and time of day. Lowering the temperature by just 1°C can save up to 6% of heating energy.
- Smart Sockets and Devices: Smart plugs can cut power to appliances in standby mode, preventing unnecessary energy consumption. This can reduce electricity bills by up to 10%.
- Water Savings
- Smart Meters and Leak Detectors: Installing smart water meters and leak detection systems helps identify and fix leaks in time, preventing excess water consumption and potential property damage.
- Aerators and Efficient Faucets: Installing aerators on taps and showerheads reduces water consumption without compromising comfort. This can lead to savings of up to 50% on water use.
- Real Savings Example
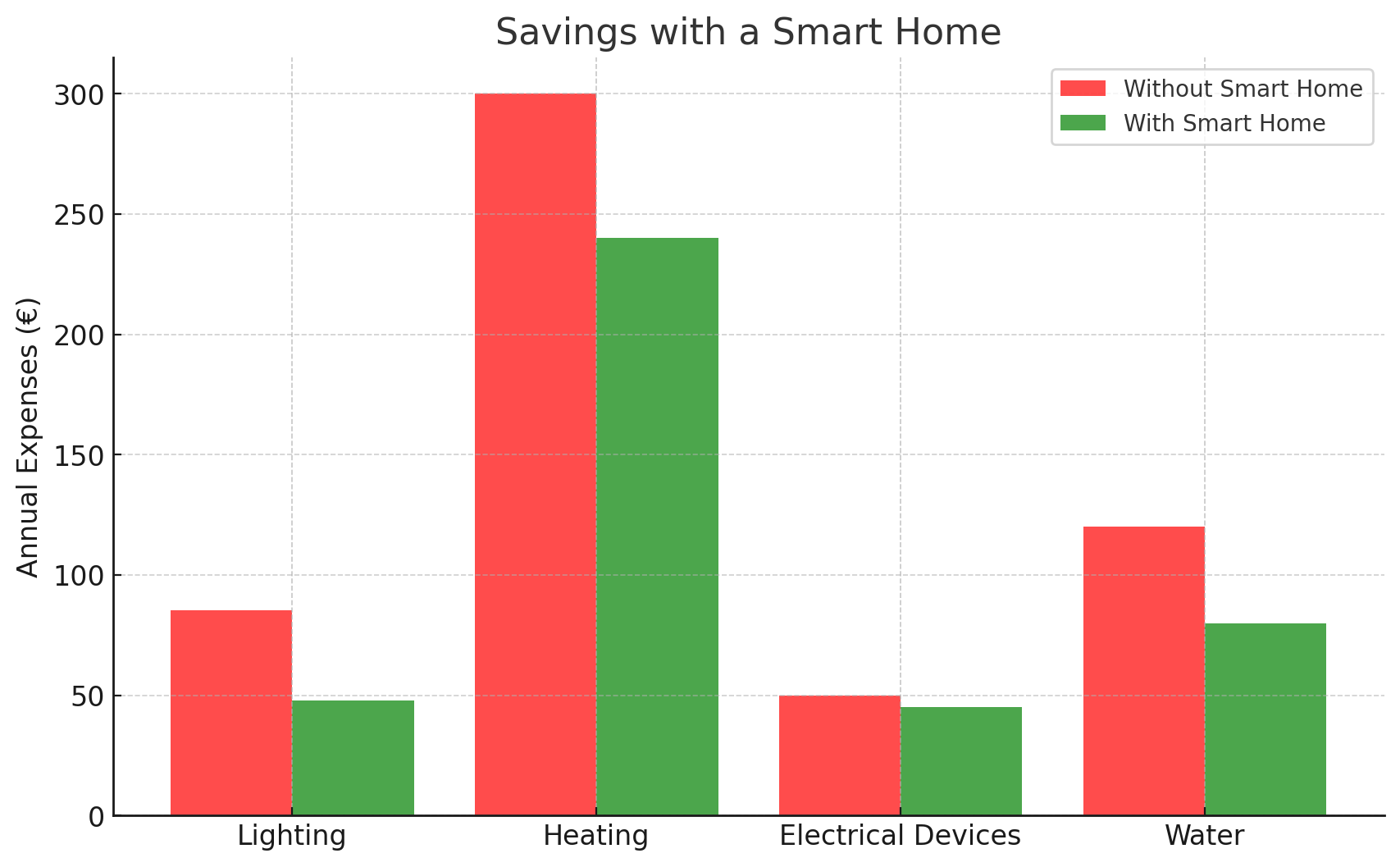
Let’s consider a house of 150 m² with 100 LED bulbs, each consuming 10W. Without a smart home system, lighting is used for an average of 5 hours per day, consuming 5 kWh daily. At a rate of €0.047 per kWh, the annual lighting cost amounts to approximately €85.41.
With a smart home system that optimizes lighting and reduces usage time, consumption can drop to 2.8 kWh per day, leading to an annual cost of €47.82. This results in savings of around €37.59 per year.
Conclusion
Integrating smart home systems significantly reduces resource consumption and utility costs. However, the efficiency depends on proper configuration and conscious use of technologies. Regular monitoring and optimization of device performance will help maximize savings and comfort in your home.